- A+
所属分类:Web前端
概述
- webpack的使用中我们会遇到各种各样的插件、loader。
- webpack的功力主要体现在能理解各个插件、loader的数量上。理解的越多功力越深
- loader是什么呢?
背景
了解loader前,我们在来看个问题,有了前面的基础我们还是用个简单的样例来说明
由于一切都是模块,我们想用js import的方式统一加载css资源
//main.js import "./main.css"; window.addEventListener("load", function () {}); //main.css body { color: aquamarine; } <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>Webpack App</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1" /> </head> <body> <h1>Hello webpack splitchunks</h1> <button id="btn1">页面1</button> <button id="btn2">页面2</button> </body> </html> 嗯,如果能这样加载就好了,我就不需要在写<style>、<link>标记了,那么是不是这么写呢
好,我们来试一下
//index.js const webpack = require("webpack"); const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require("html-webpack-plugin"); const path = require("path"); const config = { context: path.resolve(__dirname), mode: "production", optimization: { minimize: false, }, entry: "./main.js", target: ["web", "es5"], output: { clean: true, filename: "bundle.js", path: path.resolve(__dirname, "dist"), }, plugins: [ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: "index.html", }), ], }; const compiler = webpack(config); compiler.run((err, stats) => { console.log(err); let result = stats.toJson({ files: true, assets: true, chunk: true, module: true, entries: true, }) debugger }); 看下结果,有个错误,
moduleName:'./main.css'
'Module parse failed: Unexpected token (1:5)nYou may need an appropriate loader to handle this file type, currently no loaders are configured to process this file.
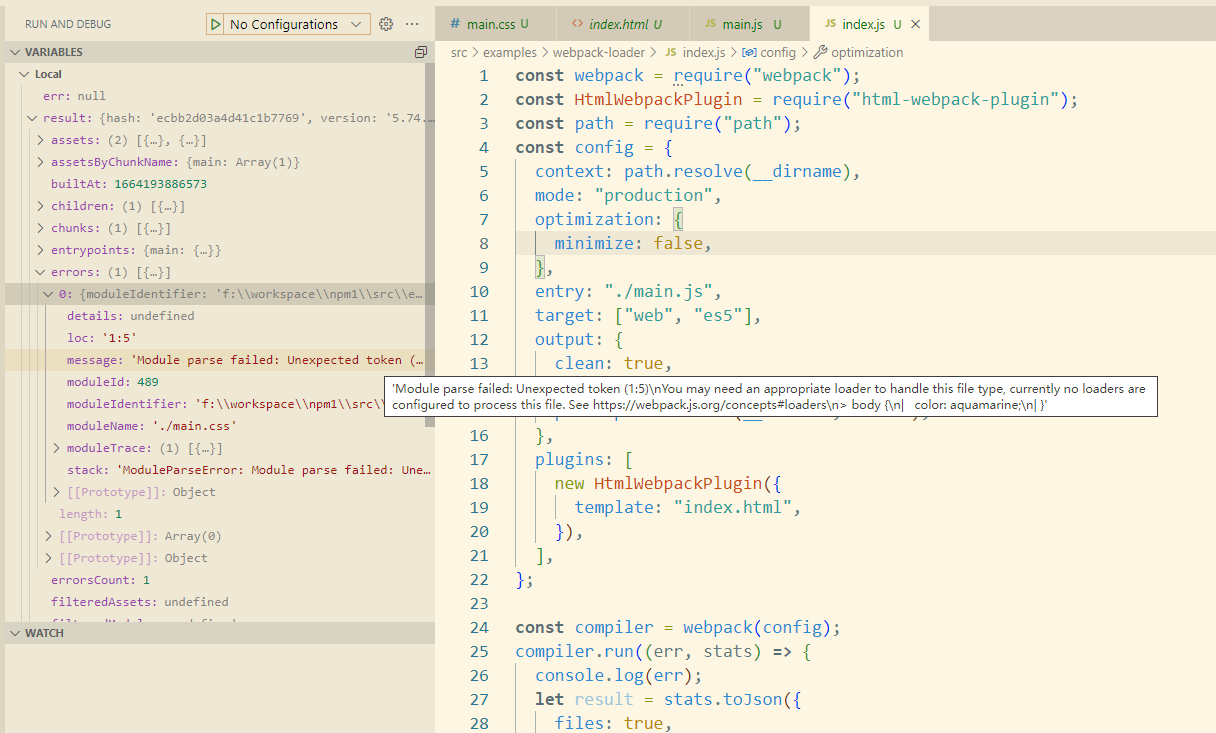
这里正是提示我们css文件不能用import的方式加载,想要加载css文件,你就需要loader
开始
先装2个loader
npm install --save-dev css-loader style-loader 添加loader配置
const webpack = require("webpack"); const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require("html-webpack-plugin"); const path = require("path"); const config = { context: path.resolve(__dirname), mode: "production", optimization: { minimize: false, }, entry: "./main.js", target: ["web", "es5"], output: { clean: true, filename: "bundle.js", path: path.resolve(__dirname, "dist"), }, plugins: [ new HtmlWebpackPlugin({ template: "index.html", }), ], module: { rules: [ { test: /.css$/i, use: ["style-loader", "css-loader"], }, ], }, }; const compiler = webpack(config); compiler.run((err, stats) => { console.log(err); let result = stats.toJson({ files: true, assets: true, chunk: true, module: true, entries: true, }) debugger }); 执行后没有了错误,页面也正常显示了
看下生成了什么代码(代码太多,截取一部分)
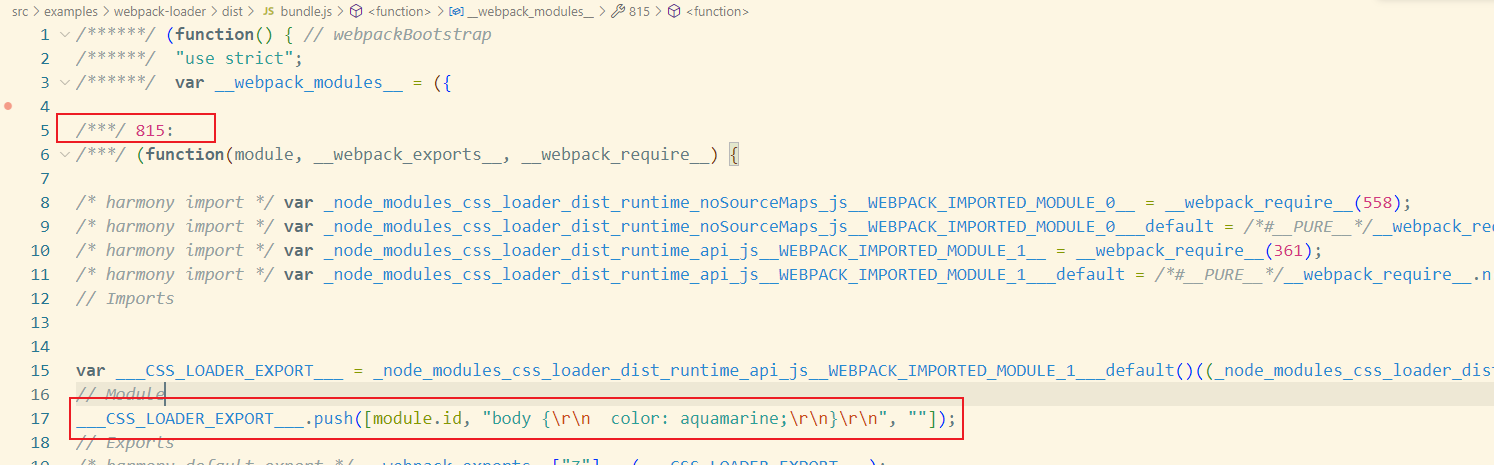
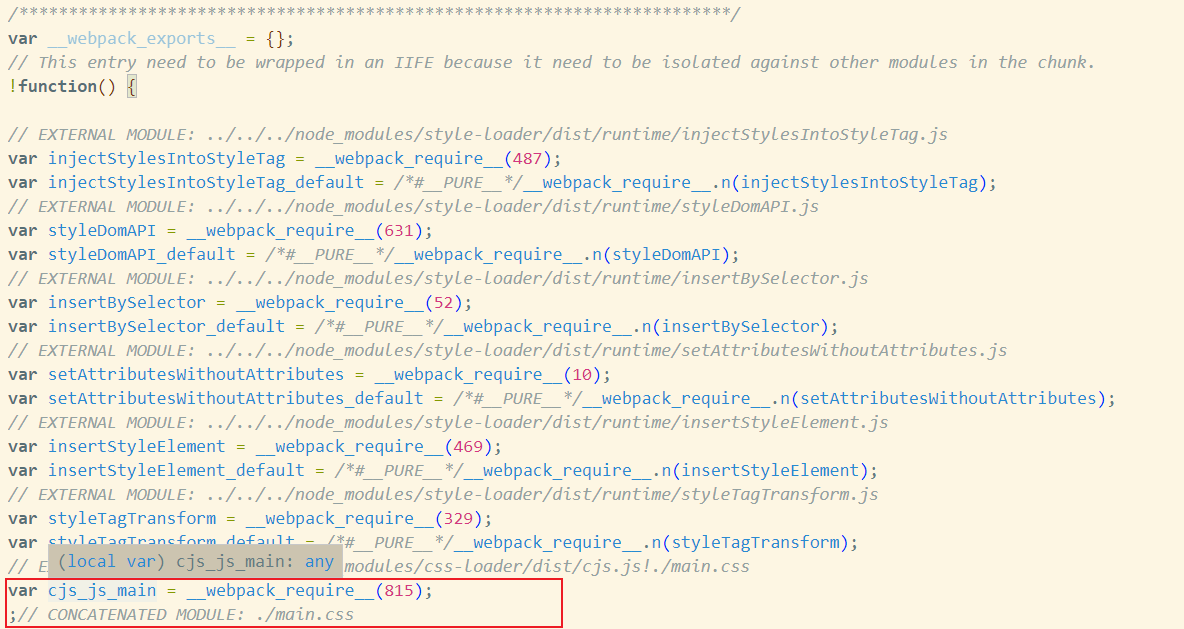
css文件居然被转换成了字符串,而且运行时会自动添加到<style>标记中
总结
- loader 可以让webpack处理更多,更丰富的文件类型,即使这个文件并不是js文件
- 有了loader的设计,webpack的应用场景强了。
- css-loader正是将我们的css文件转成了javastript的字符串
- style-loader 则帮助我们将生成的样式字符串添加的
<style>标记中,他俩配合的也真是挺到位。 - loader的设计并不局限于样式的这个场景,理解这两个loader可以让我们更深入的理解loader的设计,比如如果我想把es6语法的js文件都转成es5的js运行时,是不是也可以呢?