- A+
所属分类:Web前端
前言
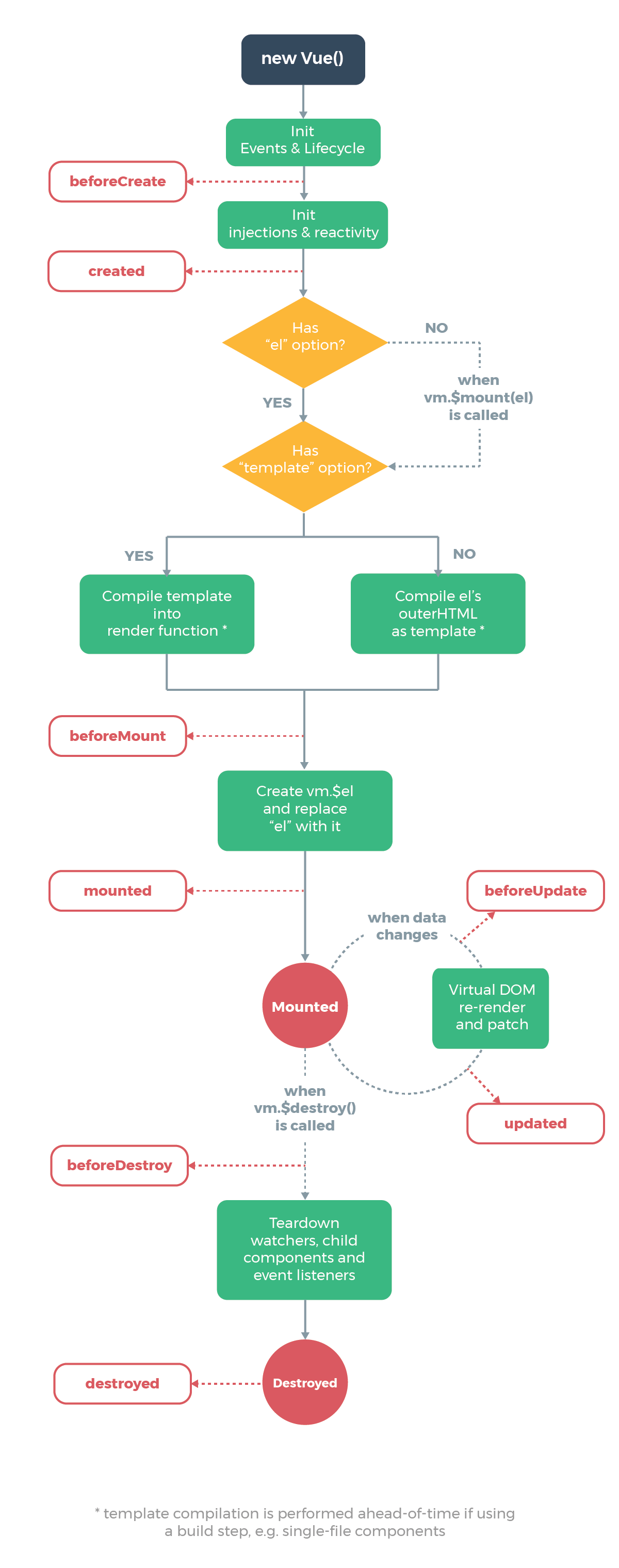
今天我们来解密下init.ts中的代码内容,并结合 vue 生命周期来分析下 vue 的初始化;
内容
init.ts
import config from '../config' import { initProxy } from './proxy' import { initState } from './state' import { initRender } from './render' import { initEvents } from './events' import { mark, measure } from '../util/perf' import { initLifecycle, callHook } from './lifecycle' import { initProvide, initInjections } from './inject' import { extend, mergeOptions, formatComponentName } from '../util/index' import type { Component } from 'types/component' import type { InternalComponentOptions } from 'types/options' import { EffectScope } from 'v3/reactivity/effectScope' // vue 实例id let uid = 0 export function initMixin(Vue: typeof Component) { // 接收实例化传入的参数 Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Record<string, any>) { //vue 实例 const vm: Component = this // 每个vue实例都有对应的一个实例id vm._uid = uid++ let startTag, endTag /* istanbul ignore if */ // 代码覆盖率测试 if (__DEV__ && config.performance && mark) { startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}` endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}` mark(startTag) } // a flag to mark this as a Vue instance without having to do instanceof // check // 标记作为vue的实例不必去执行instanceof vm._isVue = true // avoid instances from being observed // 避免实例被observed观察 vm.__v_skip = true // effect scope // 影响范围 vm._scope = new EffectScope(true /* detached */) vm._scope._vm = true // merge options // 合并参数 // 判断是否是子组件 if (options && options._isComponent) { // optimize internal component instantiation // 优化内部组件实例化 // since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the // internal component options needs special treatment. // 由于动态选项合并非常缓慢,并且没有一个内部组件选项需要特殊处理。 // 传入vue实例并进行组件初始化 initInternalComponent(vm, options as any) } else { // 根组件配置 | 合并参数 vm.$options = mergeOptions( // 解析构造函数参数 resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor as any), options || {}, vm ) } /* istanbul ignore else */ // 代码覆盖测试 if (__DEV__) { initProxy(vm) } else { vm._renderProxy = vm } // expose real self vm._self = vm // 核心的核心 // 初始化生命周期 initLifecycle(vm) // 初始化事件监听 initEvents(vm) // 初始化渲染 initRender(vm) // 调用生命周期的钩子函数 | beforeCreate callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate', undefined, false /* setContext */) // https://v2.cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#provide-inject // 在data/props前进行inject initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props initState(vm) // https://v2.cn.vuejs.org/v2/api/#provide-inject // provide 父组件提供的数据 // inject 子组件进行注入后直接使用 // 在data/props后进行provide initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props // 调用生命周期钩子函数 | created callHook(vm, 'created') /* istanbul ignore if */ // 代码覆盖测试 if (__DEV__ && config.performance && mark) { vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false) mark(endTag) measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag) } // 组件如果设置了el则挂载到指定的el上 if (vm.$options.el) { vm.$mount(vm.$options.el) } } } /** * 初始化内部组件 * * @param vm * @param options */ export function initInternalComponent( vm: Component, options: InternalComponentOptions ) { const opts = (vm.$options = Object.create((vm.constructor as any).options)) // doing this because it's faster than dynamic enumeration. const parentVnode = options._parentVnode opts.parent = options.parent opts._parentVnode = parentVnode const vnodeComponentOptions = parentVnode.componentOptions! opts.propsData = vnodeComponentOptions.propsData opts._parentListeners = vnodeComponentOptions.listeners opts._renderChildren = vnodeComponentOptions.children opts._componentTag = vnodeComponentOptions.tag if (options.render) { opts.render = options.render opts.staticRenderFns = options.staticRenderFns } } /** * 解析构造函数的选项 * * @param Ctor * @returns */ export function resolveConstructorOptions(Ctor: typeof Component) { let options = Ctor.options if (Ctor.super) { const superOptions = resolveConstructorOptions(Ctor.super) const cachedSuperOptions = Ctor.superOptions if (superOptions !== cachedSuperOptions) { // super option changed, // need to resolve new options. Ctor.superOptions = superOptions // check if there are any late-modified/attached options (#4976) const modifiedOptions = resolveModifiedOptions(Ctor) // update base extend options if (modifiedOptions) { extend(Ctor.extendOptions, modifiedOptions) } options = Ctor.options = mergeOptions(superOptions, Ctor.extendOptions) if (options.name) { options.components[options.name] = Ctor } } } return options } /** * 解析修改的选项 * * @param Ctor * @returns */ function resolveModifiedOptions( Ctor: typeof Component ): Record<string, any> | null { let modified const latest = Ctor.options const sealed = Ctor.sealedOptions for (const key in latest) { if (latest[key] !== sealed[key]) { if (!modified) modified = {} modified[key] = latest[key] } } return modified } Demo 演示
demo 位于
example/docs/01.lifecycle.html
通过debugger的方式,能够更直观的查看到整个调用的过程;这里罗列了选项式 api 和组合式 api,后续的 demo 都会以组合式 api 为主。
具体的 debugger 方法可以查看微软的文档devtools-guide-chromium,一般来说 F9 进行调试即可;如果你想跳过某一函数,那就 F10;
<script src="../../dist/vue.js"></script> <div id="app">{{msg}}</div> <script> debugger // Options API || 设置了el // var app = new Vue({ // el: '#app', // data: { // msg: 'Hello Vue!' // }, // beforeCreate() { // console.log('beforeCreate') // }, // created() { // console.log('created') // }, // beforeMount() { // console.log('beforeMount') // }, // mounted() { // console.log('mounted') // } // }) // Options API || 手动$mount // new Vue({ // data: () => ({ // msg: 'helloWord' // }), // beforeCreate: () => { // console.log('beforeCreate') // }, // created: () => { // console.log('created') // }, // beforeMount: () => { // console.log('beforeMount') // }, // mounted: () => { // console.log('mounted') // } // }).$mount('#app') // Composition API const { ref, beforeCreate, created, beforeMount, mounted } = Vue new Vue({ setup(props) { const msg = ref('Hello World!') return { msg } }, beforeCreate() { console.log('beforeCreate') }, created() { console.log('created') }, beforeMount() { console.log('beforeMount') }, mounted() { console.log('mounted') } }).$mount('#app') </script> 内容总结
这里我们总结下
init.ts中大致的内容
- 生成 vue 实例 Id;
- 标记 vue 实例;
- 如果是子组件则传入 vue 实例和选项并初始化组件,否则则进行选项参数合并,将用户传入的选项和构造函数本身的选项进行合并;
- 初始化实例生命周期相关属性,如:$parent、$root、$children、$refs 等;
- 初始化组件相关的事件监听,父级存在监听事件则挂载到当前实例上;
- 初始化渲染,如:$slots、$scopedSlots、$createElement、$attrs、$listeners;
- 调用
beforeCreate生命周期钩子函数 - 初始化注入数据,在 data/props 之前进行 inject,以允许一个祖先组件向其所有子孙后代注入一个依赖(说白了就是有个传家宝,爷爷要想传给孙子,那就要爸爸先 inject,再给儿子)
- 初始化状态,如:props、setup、methods、data(|| observe)、computed、watch
- 在 data/props 之后进行 provide
- 调用
created生命周期钩子函数,完成初始化 - 如果设置了
el则自动挂载到对应的元素上,不然就要自己$mount;




