- A+
所属分类:.NET技术
1.迭代器方法
可以使用foreach循环语句进行的迭代的方法,称为可迭代方法,或者迭代器方法。
迭代器用法法介绍。
迭代器用于依次返回每个元素,一般用于foreach循环语句。迭代器方法需要使用yield return语句。
yield return 语句介绍
保持代码的当前位置,在下一次调用迭代器方法时执行。

迭代方法在使用过程中左右步骤对应。yield return语句主要是返回一个结果作为函数调用的结果。并记录当前运行位置,当下次函数被调用时,在当前位置执行这个函数。在迭代块中除了yield return外,不允许出现普通的return语句。
迭代方法使用的命名空间为using System.Collections.Generic;
下面代码为迭代器使用的具体代码
class Program { public static IEnumerable<int> Fibs() { int f1 = 1, f2 = 2; while (true) { yield return f1; yield return f2; f1 += f2; f2 += f1; } } static void Main(string[] args) { foreach (int i in Fibs()) if (i < 20) Console.WriteLine("{0}", i); else break; Console.ReadKey(); } }
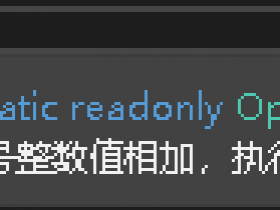
IEnumerable<int>是泛型定义的里面的int关系到你迭代对象yield return返回值的类型。如果你定义IEnumerable<int>那么你返回的值是int类型,如果你定义IEnumerable<string>那么你的返回值是string类型以此类推。如果你想以某个条件结束方法。可以使用外面的条件如上图所示。也可以使用yield break。
class Program { public static IEnumerable Fibs() { string f1 = "1", f2 = "2"; while (true) { yield return f1; yield return f2; f1 += f2; f2 += f1; if (f1.Length > 8) yield break; } } static void Main(string[] args) { foreach (string i in Fibs()) Console.WriteLine("{0}", i); Console.ReadKey(); } }
2.手动实现迭代器方法
首先是通过使用接口IEnumerable的方式,然后编写IEnumerator GetEnumerator()的方式。在代码中控制索引位置,和循环次数。如果索引位置出错则使用代码throw new NotImplementedException()报错。
using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; namespace test02 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { object [] e = new object[5] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; Itear01 s = new Itear01(e,2); foreach (object i in s) Console.WriteLine("{0}", i); Console.ReadKey(); } } public class Itear01 : IEnumerable { object[] values; int StartPoint=-1; int current=0; public Itear01(object[] values,int StartPoint) { this.values = values; this.StartPoint = StartPoint; } public IEnumerator GetEnumerator() { if(this.StartPoint==-1) throw new NotImplementedException(); while(true) { yield return this.values[StartPoint]; StartPoint = (StartPoint + 1) % values.Length; current++; if (current == values.Length) { break; } } } } }