- A+
1. 预期效果
当数据变动时,触发自定义的回调函数。
2. 思路
对对象 object 的 setter 进行设置,使 setter 在赋值之后执行回调函数 callback()。
3.细节
3.1 设置 setter 和 getter
JS提供了 [Object.defineProperty()](Object.defineProperty() - JavaScript | MDN (mozilla.org)) 这个API来定义对象属性的设置,这些设置就包括了 getter 和 setter。注意,在这些属性中,如果一个描述符同时拥有 value 或 writable 和 get 或 set 键,则会产生一个异常。
Object.defineProperty(obj, "key", { enumerable: false, // 是否可枚举 configurable: false, // 是否可配置 writable: false, // 是否可写 value: "static" }); 我们可以利用JS的 [闭包](闭包 - JavaScript | MDN (mozilla.org)),给 getter 和 setter 创造一个共同的环境,来保存和操作数据 value 和 callback 。同时,还可以在 setter 中检测值的变化。
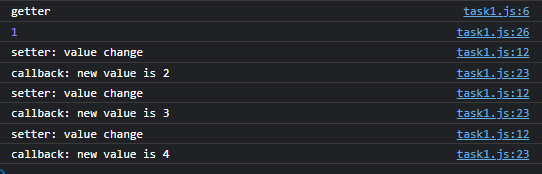
// task1.js const defineReactive = function(data, key, value, cb) { Object.defineProperty(data, key, { enumerable: true, configurable: true, get() { console.log('getter') return value }, set(newValue) { if (newValue !== value) { value = newValue console.log('setter: value change') cb(newValue) } } }); } const task = function() { console.log('running task 1...') const obj = {} const callback = function(newVal) { console.log('callback: new value is ' + newVal) } defineReactive(obj, 'a', 1, callback) console.log(obj.a) obj.a = 2 obj.a = 3 obj.a = 4 } task() 至此我们监控了 value ,可以感知到它的变化并执行回调函数。
3.2 递归监听对象的值
上面的 defineRective() 在 value 为对象的时候,当修改深层键值,则无法响应到。因此通过循环递归的方法来对每一个键值赋予响应式。这里可以通过 observe() 和 Observer 类来实现这种递归:
// observe.js import { Observer } from "./Observer.js" // 为数据添加响应式特性 export default function(value) { console.log('type of obj: ', typeof value) if (typeof value !== 'object') { // typeof 数组 = object return } if (typeof value.__ob__ !== 'undefined') { return value.__ob__ } return new Observer(value) } // Observer.js import { defineReactive } from './defineReactive.js' import { def } from './util.js'; export class Observer { constructor(obj) { // 注意设置成不可枚举,不然会在walk()中循环调用 def(obj, '__ob__', this, false) this.walk(obj) } walk(obj) { for (const key in obj) { defineReactive(obj, key) } } } 在这里包装了一个 def() 函数,用于配置对象属性,把 __ob__ 属性设置成不可枚举,因为 __ob__ 类型指向自身,设置成不可枚举可以放置遍历对象时死循环
// util.js export const def = function(obj, key, value, enumerable) { Object.defineProperty(obj, key, { value, enumerable, writable: true, configurable: true }) } 3.3 检测数组
从需求出发,对于响应式,我们对数组和对象的要求不同,对于对象,我们一般要求检测其成员的修改;对于数组,不仅要检测元素的修改,还要检测其增删(比如网页中的表格)
对由于数组没有 key ,所以不能通过 defineReactive() 来设置响应式,同时为了满足响应数组的增删改,所以 Vue 的方法是,通过包装 Array 的方法来实现响应式,当调用 push()、poll()、splice() 等方法时,会执行自己设置的响应式方法
使用 Object.create(obj) 方法可以 obj 对象为原型(prototype)创建一个对象,因此我们可以以数组原型 Array.prototype 为原型创建一个新的数组对象,在这个对象中响应式包装原来的 push()、pop()、splice()等数组
// array.js import { def } from "./util.js" export const arrayMethods = Object.create(Array.prototype) const methodNameNeedChange = [ 'pop', 'push', 'splice', 'shift', 'unshift', 'sort', 'reverse' ] methodNameNeedChange.forEach(methodName => { const original = Array.prototype[methodName] def(arrayMethods, methodName, function() { // 响应式处理 console.log('call ' + methodName) const res = original.apply(this, arguments) const args = [...arguments] let inserted = [] const ob = this.__ob__ switch (methodName) { case 'push': case 'unshift': inserted = args case 'splice': inserted = args.slice(2) } ob.observeArray(inserted) return res }) }) // Observer.js import { arrayMethods } from './array.js' import { defineReactive } from './defineReactive.js' import observe from './observe.js' import { def } from './util.js' export class Observer { constructor(obj) { console.log('Observer', obj) // 注意设置成不可枚举,不然会在walk()中循环调用 def(obj, '__ob__', this, false) if (Array.isArray(obj)) { // 将数组方法设置为响应式 Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, arrayMethods) this.observeArray(obj) } else { this.walk(obj) } } // 遍历对象成员并设置为响应式 walk(obj) { for (const key in obj) { defineReactive(obj, key) } } // 遍历数组成员并设置为响应式 observeArray(arr) { for (let i = 0, l = arr.length; i < l; i++) { observe(arr[i]) } } } 3.5 Watcher 和 Dep 类
设置多个观察者检测同一个数据
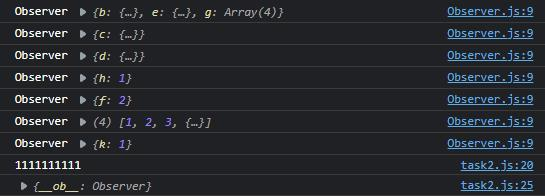
// Dep.js var uid = 0 export default class Dep { constructor() { this.id = uid++ // console.log('construct Dep ' + this.id) this.subs = [] } addSub(sub) { this.subs.push(sub) } depend() { if (Dep.target) { if (this.subs.some((sub) => { sub.id === Dep.target.id })) { return } this.addSub(Dep.target) } } notify() { const s = this.subs.slice(); for (let i = 0, l = s.length; i < l; i++) { s[i].update() } } } // Watcher.js import Dep from "./Dep.js" var uid = 0 export default class Watcher { constructor(target, expression, callback) { this.id = uid++ this.target = target this.getter = parsePath(expression) this.callback = callback this.value = this.get() } get() { Dep.target = this const obj = this.target let value try { value = this.getter(obj) } finally { Dep.target = null } return value } update() { this.run() } run() { this.getAndInvoke(this.callback) } getAndInvoke(cb) { const obj = this.target const newValue = this.get() if (this.value !== newValue || typeof newValue === 'object') { const oldValue = this.value this.value = newValue cb.call(obj, newValue, newValue, oldValue) } } } function parsePath(str) { var segments = str.split('.'); return (obj) => { for (let i = 0; i < segments.length; i++) { if (!obj) return; obj = obj[segments[i]] } return obj; }; } // task2.js import observe from "../observe.js"; import Watcher from "../Watcher.js"; const task2 = function() { const a = { b: { c: { d: { h: 1 } } }, e: { f: 2 }, g: [ 1, 2, 3, { k: 1 }] } const ob_a = observe(a) const w_a = new Watcher(a, 'b.c.d.h', (val) => { console.log('1111111111') }) a.b.c.d.h = 10 a.b.c.d.h = 10 console.log(a) } task2() 执行结果如下,可以看到成功响应了数据变化